There’s been a great deal of recent interest in the use of Blockchain technology to tackle challenges in the healthcare field, especially when it comes to maintaining compliance with the DSCSA. Beginning in November of 2023, pharmaceutical supply companies will be required to maintain accurate information that will let drugs be traced along the supply chain. The pharmaceutical industry has a huge challenge ahead of it to meet these standards, and Blockchain technology may be one of the solutions.
To understand whether or not Blockchain represents a valid solution to the issue of supply chain tracking, some background on it is necessary.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology is essentially a method of encapsulating data or information within a layered data structure so that multiple parties can trust in the accuracy of the source of information. You can think of it like a digital ledger that tracks transactions and lets multiple parties see those transactions, with an added layer of security.
The most famous use of Blockchain is to track the transactions of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but it has applications for the healthcare field including anti-counterfeiting and supply chain regulatory compliance.
How Can Blockchain Be Used To Assist In DSCSA Compliance?
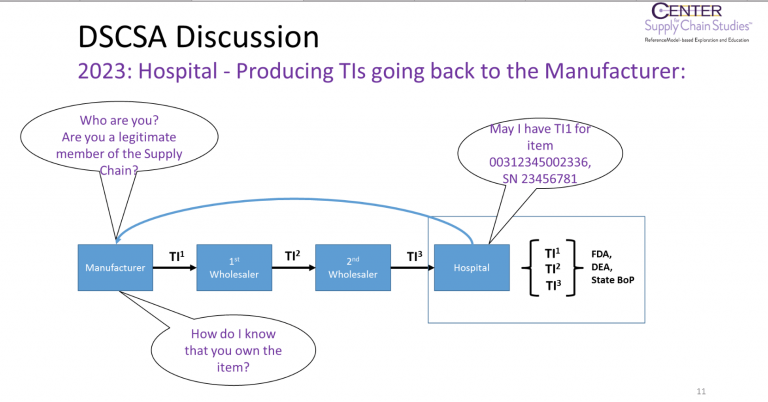
After November 27, 2023, US companies in the pharmaceutical supply chain will no longer have to give transaction histories to their customers, instead they will have to retain “…systems and processes necessary to promptly facilitate gathering the information necessary to produce the transaction information for each transaction going back to the manufacturer”.
Gathering all the documents related to transaction information would be necessary only when there is an investigation into possibly illegitimate products. This poses a problem under the new system, as many questions will be raised regarding the authenticity of the party asking for the transaction information.
If a hospital needs to gather transaction information for a drug going all the way back to the manufacturer, you can easily imagine the manufacturer asking a series of questions to see if the hospital can be trusted.
“Do you actually own the drug you’re asking for info about?” “Are you actually a trusted member of the supply chain?”
Considering what is at stake for the manufacturer, it makes sense that they would not respond to people asking for this information unless they can prove that they are trustworthy. This is a time intensive and frustrating process, and the law allows only so much time to provide the required transaction information.
This is where Blockchain comes in as a possible solution to this problem. Blockchain introduces a way of ensuring that the party making a request for information can be trusted, that their reason for requesting the information is legitimate, and that they own the product they are asking about.
Let’s take a closer look at the key features of Blockchain and the difficulties in implementing the DSCSA.
Why Is Blockchain So Helpful In Meeting DSCSA Challenges?
The Center for Supply Chain Studies (C4SCS) is an organization created to assist different industries in evaluating the impact of changes in regulatory, business, or technological areas. A team from the C4SCS conducted an in-depth investigation of the challenges in industry compliance with the new DSCSA standards, and if Blockchain could assist in solving these issues.
Here’s a rundown on the challenges of meeting compliance for DSCSA, as identified by the C4SCS:
- There’s a distributed environment with a wide variety of companies and parties in the industry
- There’s a need to share data with unknown participants in the supply chain
- A massive amount of data exists to be collected and stored
- Current proposed solutions to DSCSA compliance are expensive and intrusive, largely relying on adequate funding and governance to ensure compliance
And here are some of the key features of Blockchain that make it attractive:
- Blockchain is distributed, with no central authority
- Blockchain is also anonymous, and anyone can participate in it at any time
- There’s a single point of entry involved in Blockchain, which makes connection easy. It’s also private, and you don’t need everyone to know when you’ve entered Blockchain
- It’s safe and trustworthy
- Blockchain is self-funded, it generates income for the parties which perform the services necessary
It’s easy to see that the features of Blockchain align nicely with the DSCSA and provide possible solutions to its issues. The problem of a distributed environment is handled by the fact that Blockchain itself is also distributed, yet secure and trustworthy. Blockchain gives people a way of trusting other parties without needing a central repository or governing agency to oversee everything and would work whether or not a distributed or centralized architecture was used.
Blockchain’s Adoption Problems
The C4SCS team is convinced that Blockchain represents a viable solution to the problems posed by the new DSCSA standards. However, there are issues preventing widespread adoption of Blockchain.
Blockchain is still a rather new technology and lacks the technical standards that would encourage wide acceptance of the platform. For this reason, many industry observers feel that it is still too early to pursue commercial applications for Blockchain. That said, there is an intense interest and energy around Blockchain that will spur further development of the technology and of its standards, so it is possible that by 2023 the technology will have advanced far enough to make Blockchain the obvious solution to the DSCSA’s compliance issues.
About TrackTraceRx Suite
Other solutions on the market today are totally fragmented by only providing one piece of the puzzle. Pharmaceutical companies today are stuck subscribing to multiple services, accessing different companies for support and paying thousands of dollars to integrate different systems. The TrackTraceRx Suite is a game changer by combining the TrackTraceRx Traceability Solution, a ERP, and a Commerce Platform completely integrated out of the box. This eliminates having to deal with multiple support, feature services and integration costs.